How Resume Parsing Transforms Hiring

How Resume Parsing Transforms Hiring
What is Resume Parsing and Why It Matters
Resume parsing is the automated process of converting free-form resume documents (such as PDFs, Word files, and images) into structured, machine-readable data. By using technologies like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Natural Language Processing (NLP), parsers extract critical information—contact details, work history, skills, and education—and populate them directly into an Applicant Tracking System (ATS).
For recruiters, this technology is the difference between data entry and talent acquisition. Instead of manually typing candidate details, parsing allows hiring teams to focus on engagement and decision-making.
Consider the alternative: the "black hole" of recruitment data. Without parsing, resumes exist as static images. They cannot be searched, filtered, or analyzed. A recruiter might remember seeing a "Python developer" last week, but without structured data, finding that specific file among hundreds is impossible. Resume parsing solves this by turning documents into a searchable database, unlocking speed, consistency, and reduced bias.
The Cost of Manual Entry
To understand the value of parsing, we must first look at the inefficiency it replaces. Meet Sarah, a senior recruiter at a mid-sized tech firm. Her Monday morning begins with a new job opening for a "Product Manager." By Tuesday, she has 250 applications.
Without an effective parser, Sarah’s workflow is manual. She opens a PDF, scans for the candidate’s name, switches tabs, types it into her spreadsheet or legacy system, switches back to find the email, types that, and then tries to interpret the work history. It takes her roughly five minutes to process a single resume. For 250 applicants, that is nearly 21 hours of non-strategic administrative work just to create a shortlist.
Real-World Scenario: The Screening Bottleneck
Let’s look closer at Sarah’s scenario to see exactly where the hiring process breaks down without automation.
The Manual Workflow Nightmare
In Sarah's manual workflow, the problems compound quickly. Because she is overwhelmed by the volume, she starts skimming faster, spending only 6–8 seconds per resume. This speed leads to cognitive fatigue.
- Inconsistency: She rejects a candidate at 9:00 AM for lacking a specific keyword but accepts a similar candidate at 4:00 PM because she’s worried about low pipeline numbers.
- The "Apply" Wall: On the candidate side, the application form requires them to upload a resume and then manually re-enter their work history. Data shows that up to 60% of job seekers abandon applications when faced with this redundancy. Sarah isn't just losing time; she's losing the best talent who refuse to jump through administrative hoops.
- Data Hygiene: Because the data is entered manually, typos are rampant. Phone numbers are incorrect, and skills are misspelled (e.g., "Project Managment"), making future searches useless.
The Parsing Intervention
Now, imagine Sarah’s company implements a modern hiring stack with a robust resume parser (like those found in platforms such as Foundire). The workflow changes instantly.
When a candidate uploads a PDF, the parser acts immediately. It identifies that "Aug 2020 – Present" is a date range and links it to "Senior Product Manager." It recognizes "Agile," "Scrum," and "JIRA" not just as text, but as Skill entities.
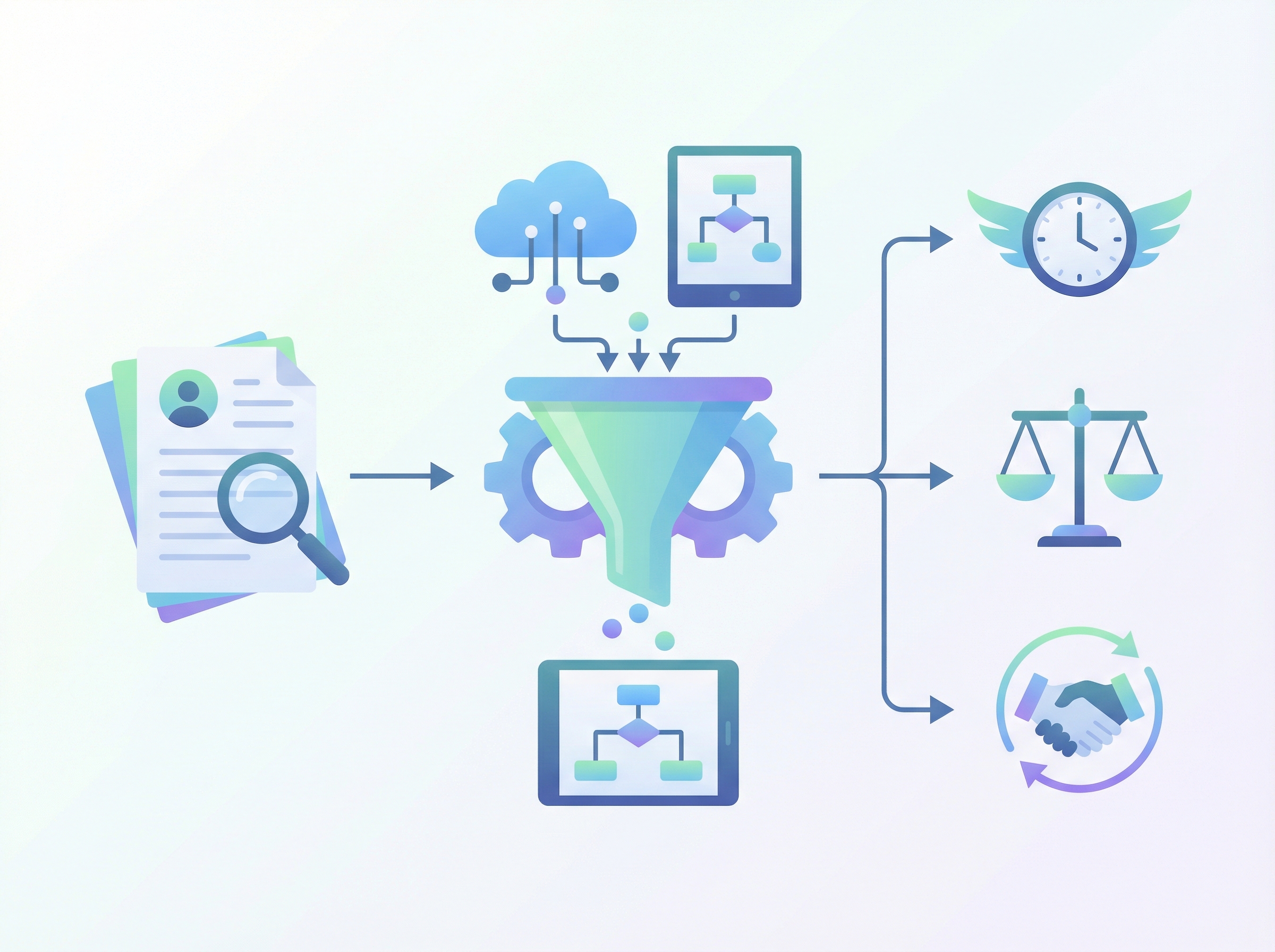
Instead of 21 hours of data entry, the system processes all 250 resumes in under five minutes. Sarah logs in to find a ranked list of candidates who meet the "Must-Have" criteria. Her time is now spent reviewing the top 20% of applications in depth, rather than skimming 100% of them frantically.
Core Insights and Best Practices
To get the most out of resume parsing, recruiters and hiring leaders need to treat it as a strategic tool, not just a backend utility. Here are actionable heuristics to optimize your usage.
Actionable Heuristics
- Calibrate for "Skills," Not Just Keywords: Modern parsers use semantic analysis. They know that "React.js" and "ReactJS" are the same skill. Ensure your ATS is set up to map these variations to a single canonical skill tag. This drastically reduces false negatives.
- Use Parsing to Power Structured Interviews: Don’t let the parsed data die in the ATS. Use the extracted skills and experience gaps to auto-generate interview scorecards. If the parser detects a 2-year employment gap, the system should flag this for the screening call.
- Validate with "Human-in-the-Loop": While AI accuracy is high (90%+), it isn't perfect. Implement a "Review" step where the candidate verifies their parsed data before final submission. This shifts the validation effort from the recruiter to the candidate, ensuring 100% accuracy without recruiter burnout.
Common Pitfalls
Warning: The most common mistake is over-reliance on exact matching. If your parser is set to reject anyone missing the exact phrase "Customer Service Representative," you will miss excellent candidates who wrote "Client Success Specialist." Always configure your system to look for semantic equivalents.
- Ignoring PDF vs. Word nuances: While modern OCR is powerful, complex graphics, two-column layouts, and tables in PDFs can still confuse simpler parsers. Advise candidates to use standard, single-column formats for the best results.
- The "Frankenstein" Profile: Sometimes a parser will merge two different jobs if the dates aren't clearly separated. Recruiters must quickly visually scan the "parsed" view against the "original" view during the final offer stage to ensure background checks are accurate.
The Breakthrough: Measuring Impact
The turning point in any recruitment function comes when resume parsing is fully operationalized. The shift is measurable and dramatic.
Before and After Analysis
Before parsing, the "Time-to-Shortlist" metric might hover around 5–7 days. With parsing, this drops to near-zero. But the real breakthrough isn't just speed; it's quality of hire.
By automating the initial screen, recruiters like Sarah can engage with candidates effectively immediately after they apply. Speed is a competitive advantage; the first company to interview a top candidate often wins them. In a recent analysis of high-volume hiring teams, implementing automated parsing and scoring increased the interview pass-through rate by 15% because recruiters were only speaking to candidates who were already verified to have the requisite skills.
Efficiency Metrics
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) improved by parsing include:
- Candidate Drop-off Rate: Reduced significantly (often by half) when "Quick Apply" is enabled via parsing.
- Cost Per Screen: If a recruiter's time is valued at $50/hour, saving 20 hours per role saves $1,000 in operational costs for a single vacancy.
- Database Reactivation: Parsed data remains searchable. Six months later, when a new role opens, Sarah doesn't have to pay for a new job ad. She searches her own database for "Product Manager" and finds the silver medalists from the previous round instantly.
Strategic Value for Recruiters
Mastering resume parsing technology is a career differentiator for talent professionals. It moves you from being a "resume reviewer" to a "talent operations architect."
Career Differentiation
When interviewing for Head of Talent roles, being able to articulate how you reduced time-to-fill using technology is powerful. You aren't just finding people; you are building scalable systems.
Q: “How have you applied resume parsing to improve outcomes?”
A: "I transitioned our team from manual reviews to an automated parsing workflow. This standardized our data entry, reduced unconscious bias by focusing on skills rather than schools, and reduced our time-to-shortlist by 70%, allowing us to close senior roles two weeks faster."
Resume Bullets for Your Own CV:
- Implemented AI-driven resume parsing, reducing administrative screening time by 15+ hours per week.
- Optimized ATS data architecture, improving candidate searchability and database reactivation rates by 40%.
- Designed a "Quick Apply" workflow that increased applicant conversion by 25% while maintaining data integrity.
Pros & Cons
| Benefit | Tradeoff |
|---|---|
| Speed & Scale: Processes thousands of applications instantly, enabling high-volume hiring without adding headcount. | Formatting Sensitivity: Highly creative resumes (infographics, charts) can still cause parsing errors, potentially rejecting qualified creatives. |
| Bias Reduction: Can be configured to blind specific fields (name, university) to focus purely on skills and experience. | Keyword Rigidity: If not calibrated correctly, it may filter out non-traditional candidates who have the skills but lack the specific industry jargon. |
| Better Analytics: Turns documents into data, allowing for reporting on "source quality" and "skills supply." | Cost: Enterprise-grade parsing solutions are an investment and require initial setup time to map fields correctly. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is resume parsing?
Resume parsing is the technology that automatically scans a resume (PDF, Word, etc.) and extracts structured information like contact details, skills, work history, and education into a database or ATS. It eliminates manual data entry.
Can resume parsing backfire?
Yes, if the parser is too rigid or the resume is poorly formatted (e.g., using graphics or tables), valid candidates can be rejected. This is often called a "false negative." It is crucial to use semantic matching rather than just keyword matching.
How do parsers handle PDF vs. Word documents?
Modern parsers handle both well, though Word documents are generally easier to parse accurately because the text structure is simpler. PDFs require OCR (Optical Character Recognition), which can sometimes struggle with unusual fonts or multi-column layouts.
Does AI resume parsing reduce hiring bias?
It can. Parsers can be configured to "blind" or hide personal information (like names, photos, and addresses) from the initial view, forcing recruiters to evaluate candidates solely on their skills and experience.
Conclusion
Resume parsing is no longer just a "nice-to-have" feature; it is the foundation of a modern, scalable hiring engine. By transforming static documents into dynamic data, companies can hire faster, reduce bias, and treat every candidate with the respect of a timely response. The recruiters who master this technology will not be replaced by AI—they will be the ones orchestrating it.
Clean data leads to better decisions. If you want to operationalize resume parsing with structured workflows—from sourcing and screening to AI interviews and scorecards—try tools like Foundire (https://foundire.com) to build a seamless, data-driven hiring process.





